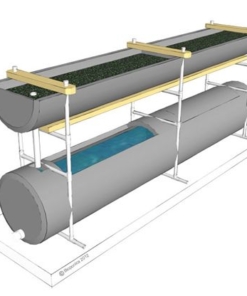
Making Fertilizer
What is Bioponics?
Organic Hydroponics? Or Aquaponics Without the Fish?
Here's how bioponics is similar to both hydroponics and aquaponics:
- Bioponics is soilless, utilizing one or more of the following techniques; FD -flood and drain or EF ebb and flow with media beds, NFT-nutrient film technique in trickling troughs, DWC-deep water culture on floating rafts and the ALT air layer technique on stationary rafts with EF ebbing and flowing water levels.
- Bioponics is 100% organic. No manufactured petro-chemical fertilizers, pesticides or herbicides.
- With bioponics, fish are optional. Herbivore fish such as tilapia and crawfish do particularly well in bioponic systems, as they are treated more like pond fish, deriving nutrients from biomass teas and aquatic organisms including algae, microbes and duckweed. Raising fish is encouraged but dependency on fish waste is an aquaponics approach, not bioponics.
How is it different from organic hydroponics and aquaponics?
- 'Organic hydroponics' is rarely 100% organic. When organics are used they are done so with additional inputs from mined minerals and or adjusted pH with chemicals etc Typically hydroponics does not have enough biofiltration or appropriate plumbing to support an entirely organic fertilizer.
- Fish are not necessary with bioponics. The reason is because both systems start with one form of organic biomass as the source of nutrients. With aquaponics, inorganic nutrients are produced from fish urine which is produced after fish consume the organic feed. With bioponics, the same inorganics are produced entirely from microbes. Bioponics encourages microbes that convert the organic carbon from biomass fertilizer into inorganic minerals and into CO2 (just like fish).
- Aquaponics almost always requires additional minerals, typically inorganic from salt mines. That is because fish foods, and fish, do not contain high levels of minerals needed for growing most heavy feeding and flowering plants. For this reason, aquaponics typically use 'base tanks' that are maintained in addition to fish tanks. Base tanks contain alkaline minerals that are infused into the grow beds, in combination with the ammonia and nitrogen from the fish tanks.
Bioponica systems for Aquaponics, Hydroponics and Bioponics:
Making Fertilizers for Bioponics:
The quality of fertilizer nutrients derived from plant derived biomass is superior to petrochemical and mined mineral salt fertilizers.
Bioponica has developed a process of producing liquid fertilizers as a substitute to fish waste and hydroponic nukes. The process involves a combination of anaerobic extraction and aerobic biofiltration with vortex aeration.
We call this process nutricycling. Because it is focused on making extracts that are ideal for plant growth, the nutrient levels of NPK nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium is optimized for plants moreso that aquaponics fish foods, which are optimized for growing fish. Biomasses may be blended for various levels of NPK plus other nutrients that are naturally present in biomass. Our blends are called Primordial Soup dry blends. Growers can take these blends and exctract them into water for use in soilless grow system or for fertigation directly into the soil for in-ground growing.
By definition "bio" ponics is 'biological.' The benefit of this technique is that by growing entirely with organic nutrients, beneficial microbes colonize on and around the plant roots. This aids in biofiltration and improves fertilizing nutrient uptake. Bioponics does not allow for the use of chemical fertilizers. Because of that it is distinct from hydroponics, a soilless technique that primarily uses inorganic fertilizers.
Plant derived biomass leachate provides an ideal balance of trace elements, amino acids, carbohydrates, vitamins, enzymes and plant hormones. Furthermore, there is no buildup of EC electrical conductivity in bioponics because biomass does not typically contain chlorides greater than what the plant requires. For that reason, there is no discharge of water required to maintain balance in bioponics. These features of NPK control, organic fertility and no toxic residue illustrate the viabilityof bioponics as a more sustainable alternative to both aquaponics and hydroponics.
Some growers attempt to grow hydroponically with organic fertilizers but unless there are measures taken to oxidize (heavily aerate) and/or biofilter organic carbon, the 'sterile' hydroponic environment will go anaerobic and plants suffer. The Biogarden is a Bioponica growing system that accommodates optimal organic growing conditions for plants, with or without fish. And, it simultaneously acts to create liquid fertilizer from biomass teas. We use the natural forces of the vortex to oxygenate the enriched water and a blended grow media microbes s for biofiltration.
As with the best soil care, bioponics is about nourishing the diverse array of living organisms that support the plant roots. The more common, and important microbes in the organic garden include nitrifiyers and decarboxylators along with rhizobacteria, microrhizomes, protozoans, nematodes and earthworms. These are the heart of the food web, cycling nutrients from plant derived organics and releasing into plant-ready 'inorganics'.
Plant derived organic fertilizer teas for bioponics also provides a health dose of trace minerals, vitamins, hormones and growth factors to the plant roots.
Bioponics is similar to both hydroponics and aquaponics in that it is soilless. As demonstrated with aquaponics, it is possible to grow plants organically without soil. And yet, bioponics is able to provide more nutrients than aquaponics because there are more options for nutrient inputs than simply fish feed and the fish waste bioproducts. There is also more tolerance in a bioponic system for concentrating nutrients, such as ammonia and BOD's (biological oxygen demand - carbon), without harming the fish which require a minimum of oxygen.
The various soilless environments known for raising plants in hydroponics and aquaponics are also possible with bioponics. This includes DWC deep water culture, flood and drain or ebb and flow media beds and NFT nutrient film technique.
Fish are suitable bioponics. In fact they are encouraged. They are easy to raise and do not require the same attention as when growing fish for the purpose of making fertilizers. Interestingly, herbivores such as carp, tilapia and crustaceans can be raised on carbon rich leachates derived from the biomass anaerobic exctraction process. Biofiltration removes the carbon, so less biofiltration is utilized when growing both plants and fish together.
When raising fish with bioponics there is a greater range of products that may be used as biomass to feed them, and it is easier to use an organic derived feed. Aquaponics may be classified as "organic" but the fish are not, unless they are fed an organic biomass derived leachate.
In addition to the leachates and detritus of decomposing grasses, biomasses and food discards, herbivore and omnivore fish can also be fed duckweed and earthworms, which are among the polyculture of a bioponic growing operation.
But they are not required. Many proud aquaponics farmers are confused by what we propose is the difference between aquaponics and bioponics This is a key distinction.
From my own experience, raising fish to feed plants organically is not a practical arrangement. Fish like and alkaline environment, plants prefer more acidic. Fish are stressed in aquaponics settings being that they are crowded and have to compete for periodic feedings. For the record, when feeding fish leachate from biomass extraction, the liquid within the water is a non-competitive feeding experience. Merely swimming or movement of nutrient rich water through the gills is how feeding takes place in carbon rich water tanks, as it is in fertile pond and marine settings.
Biomass Blends for Making Liquid Fertilizer
More about Hydroponics and Aquaponics vs Bioponics:
Hydroponics is popular as it conserves water use through soilless recirculating growing techniques. And, plant growth is optimized by managing NPK and PPM of chemical fertilizers. These are the primary hydroponic benefits, yet to manage EC-electrical conductivity, chloride contaminants from manufactured mineral elements must be plunged from the system and disposed of into the environment. There is no EC buildup or water discharged in bioponics.
Aquaponics is also soilless. It performs well for green leafy plants, and does so by using fish feed and fish urine as a source of nutrient inputs. It does not, however, do so well for fruiting or heavy feeding vegetables and herbs. That’s due to the challenge in simultaneously optimizing the conditions for plants and fish which have different environmental needs. Fish like alkaline water, plants need more acidic. More potassium and phosphorus is needed than that which is produced from the fish urine in the alkaline pH environment. And it’s difficult to regulate concentration of fish urine nutrients to ideally satisfy plant needs through different stages of growth.
Electrical conductivity is a major concern with hydroponics growing. This is mostly do to the use of chemical fertilizers that contain chloride salts. The chloride element contributes a persistent negative ionic charge which raises the electrical conductivity of the hydroponic solution. Chloride 'creeps up' in the solution because it is not appreciably taken up by the plants. Excessive chloride buildup or an increased EC impedes plant uptake of the critical fertilizer nutrients. In fact the plant literally dehydrates when EC electrical conductivity rises so high that the chloride osmotic forces draw water from the plant roots and wilt the plant.
Mined or manufactured potassium, calcium and magnesium contain chlorides which increase EC electrical. Chlorides are the primary reason HCL, hydrochloric acid, is not recommended for lowering pH in hydroponic systems.
The treatment used to reduce chloride buildup in hydroponic systems is reverse osmosis, which gets expensive in larger systems, or periodic water discharge, which is inefficient and bad for the environment.
With bioponics unless source water has high chlorides there is no buildup of EC electrical conductivity. That's because plant derived potassium, calcium and magnesium are mobilized from organics extracts and contains relatively few chlorides, only what the plant needs. For that reason, there never is a buildup of EC electrical conductivity with bioponics. This means fertilization water is never discharged and the process of managing fertilization is much easier...more natural.
Using the Bioponica process of Nutricycling™ allows for tight control of NPK and PPM’s with bioponics. The quality of fertilizer teas derived from plant derived biomass is superior to manufactured fertilizers. They provide an ideal balance of trace elements, amino acids, carbohydrates, vitamins, enzymes and plant hormones. Furthermore, there is no buildup of EC electrical conductivity in bioponics because biomass does not typically contain chlorides greater than what the plant requires. For that reason, there is no discharge of water required to maintain balance in bioponics. These features of NPK control, organic fertility and no toxic residue illustrate the viability of bioponics as a more sustainable alternative to both aquaponics and hydroponics.